Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteoporosis
Overview of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease
characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue and bone
structure, which can lead to increased bone fragility and risk of fracture.
The most common fractures associated with osteoporosis are in the hip, spine, wrist, and shoulder.
Osteoporosis is the major cause
of fractures in postmenopausal women and in older men. Fractures can occur in
any bone but happen most often in bones of the hip, vertebrae in the spine, and
wrist.
Early diagnosis and treatment of
osteoporosis is essential to help prevent fragility fractures, which can cause
severe pain, long-term disability, and early mortality. The goals of
treatment of osteoporosis are to preserve bone mass, prevent fractures,
decrease pain, and maintain function.
What are the symptoms &
signs of Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis symptoms can include:
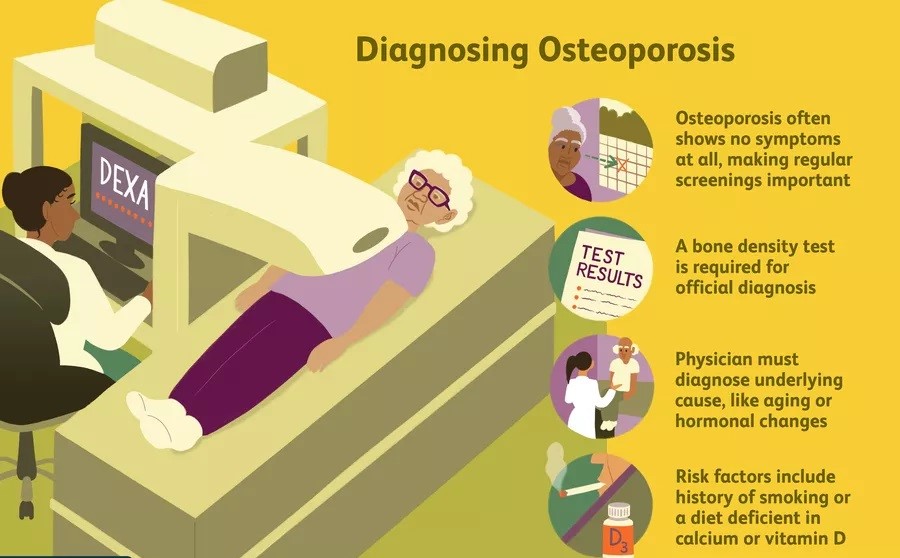
Usually, there are no symptoms of
osteoporosis. That is why it is sometimes called a silent disease. However, you
should watch out for the following things:
- Loss of height (getting shorter by an inch or more).
- Change in posture (stooping or bending forward).
- Shortness of breath (smaller lung capacity due to
compressed disks).
- Bone fractures.
- Pain in the lower back.
Osteoporosis signs can include:
- Severe back pain
- Loss of height over time
- A stooped posture
- Bone fractures from minor injury
Doctors Liked to Read More
Clinical Exams
- Medical history
- Physical examination
- Laboratory tests (Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin-D, calcium, phosphate, magnesium, alkaline phosphatase, creatinine and thyroid-functions test)
- Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA or DXA) for Bone
Mineral Density (BMD)
The following procedures can be
performed to determine bone fractures due to osteoporosis:
- Bone x-ray
- CT scan of the spine
- MRI of the spine
Risk factor modification
·
Proper nutrition.
·
Lifestyle changes.
·
Sunlight exposure.
·
Exercise.
·
Fall prevention to help prevent fractures.
Medications
·
Calcium and vitamin D supplements
·
Bisphosphonates (alendronate, risedronate,
ibandronate, zoledronic acid)
·
Raloxifene and bazedoxifene
·
Teriparatide and abaloparatide
·
Denosumab
·
Romosozumab
·
Hormone replacement therapy
For treatment and prevention, ensure adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D, using supplements when necessary, and modify risk factors to help preserve bone mass (eg, with weight-bearing exercise and by minimizing use of caffeine, alcohol, and tobacco).
The rate of bone loss can be slowed with drugs, but adequate Calcium and Vitamin D supplements and Physical activity are critical to maintaining optimal bone density.





Comments
You must login to write comment